Avoid Excessive Use of Contact Lenses: Key Tips for Preventing Eye Infections and Complications
Contact lenses, ultra-thin lenses placed directly on the eye's surface, have garnered popularity as a preferred alternative to traditional glasses for a multitude of reasons. Beyond offering improved peripheral vision compared to glasses, these lenses are valued for their convenience, especially during sports activities. Their aesthetic benefits can boost self-esteem in teens and children, positively influencing their performance in various endeavors. Nevertheless, judicious use of contact lenses is paramount due to the potential risks of microbial infections, corneal ulcers, eye infections, and even sight-threatening conditions like blindness. A critical aspect of responsible contact lens usage is adhering to the recommended duration of wear. Lenses come in various disposal schedules, including daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly. Overuse of contact lenses poses a significant risk. While standard hours of wear range between 8 to 12 hours, exceeding this duration can have dire consequences. Globally, over 150 million individuals utilize contact lenses, employing them for vision correction, cosmetic enhancements, and therapeutic indications in cases of specific eye conditions, such as impending corneal perforation.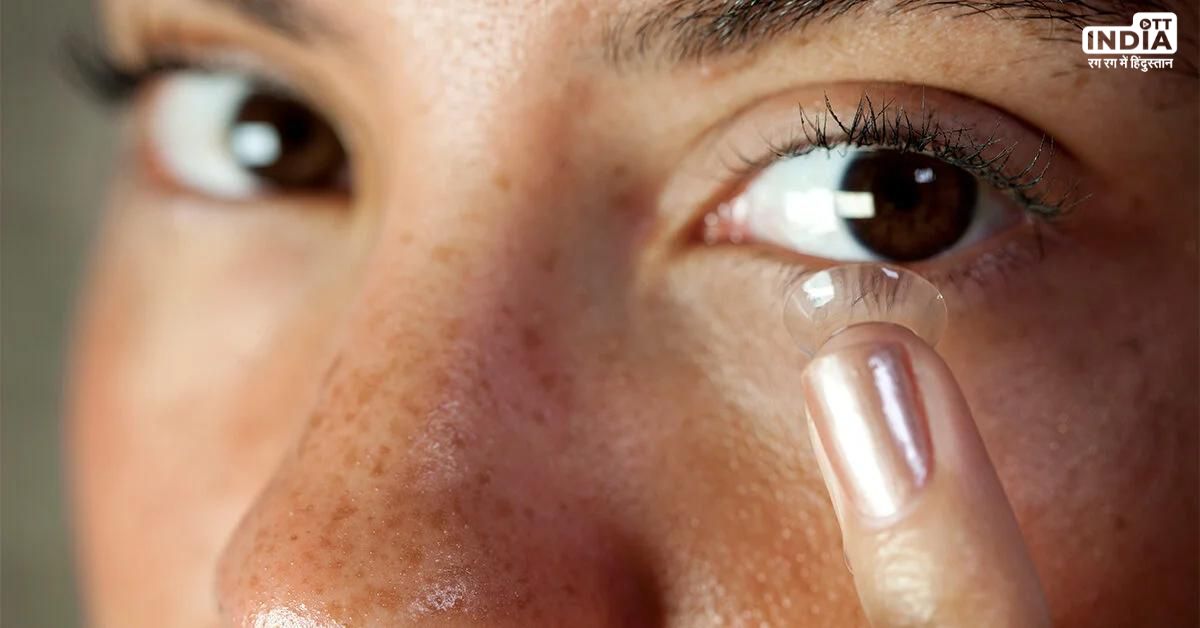  Contact lens-related complications are a cause for concern, albeit largely preventable through proper usage practices. Around 5% of wearers experience complications annually, often stemming from poor lens care practices. Inadequate hygiene fosters bacterial, fungal, and microbial infiltration on the lens, which can escalate into severe eye complications, including corneal issues and compromised vision. To mitigate these risks, certain guidelines should be followed:
Contact lens-related complications are a cause for concern, albeit largely preventable through proper usage practices. Around 5% of wearers experience complications annually, often stemming from poor lens care practices. Inadequate hygiene fosters bacterial, fungal, and microbial infiltration on the lens, which can escalate into severe eye complications, including corneal issues and compromised vision. To mitigate these risks, certain guidelines should be followed:
 Contact lens-related complications are a cause for concern, albeit largely preventable through proper usage practices. Around 5% of wearers experience complications annually, often stemming from poor lens care practices. Inadequate hygiene fosters bacterial, fungal, and microbial infiltration on the lens, which can escalate into severe eye complications, including corneal issues and compromised vision. To mitigate these risks, certain guidelines should be followed:
Contact lens-related complications are a cause for concern, albeit largely preventable through proper usage practices. Around 5% of wearers experience complications annually, often stemming from poor lens care practices. Inadequate hygiene fosters bacterial, fungal, and microbial infiltration on the lens, which can escalate into severe eye complications, including corneal issues and compromised vision. To mitigate these risks, certain guidelines should be followed: - Adhere to prescribed wearing schedules.
- Refrain from sleeping with lenses on.
- Limit daily wear according to medical advice (8-12 hours).
- Respect the recommended disposal frequency.
- Allow the eyes to breathe by removing lenses periodically.
- Protracted use of contact lenses, particularly without breaks, can lead to diminished oxygen supply to the cornea, resulting in dry eye syndrome.
- The cornea relies on atmospheric oxygen to maintain its transparency, making prolonged wear a catalyst for discomfort and blurred vision.
- Additionally, extended use increases vulnerability to eye infections, fostering the growth of bacteria, fungi, and microorganisms, leading to corneal infections and potential scarring.
- Long-term usage, exceeding 10 hours daily for more than 5 years, can trigger complications such as decreased corneal thickness and altered curvature.
Next Story