Emerging Diseases and Outbreaks: Vigilance in the Face of Threats
In an interconnected world, emerging infectious diseases pose a significant and constant threat to global health security. While COVID-19 has been the most prominent example in recent times, other diseases like Zika and Ebola have shown us that new pathogens can rapidly spread, causing devastating outbreaks. Let's explore the ongoing challenges of emerging diseases and outbreaks and the crucial importance of preparedness and global cooperation.
The Unpredictable Nature of Emerging Diseases:
Emerging diseases are often caused by pathogens that jump from animals to humans, a phenomenon known as zoonosis. These diseases can emerge anywhere in the world, often in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure. They can spread quickly, thanks to increased travel and globalization, making them a global concern.
The Zika Virus Outbreak (2015-2016):
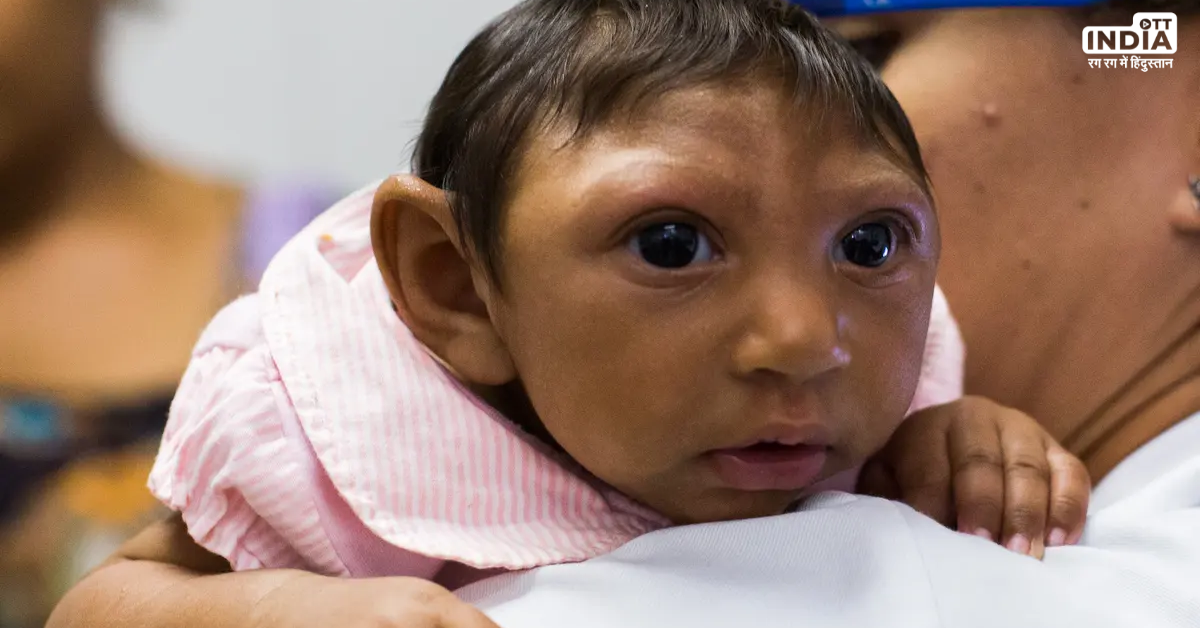
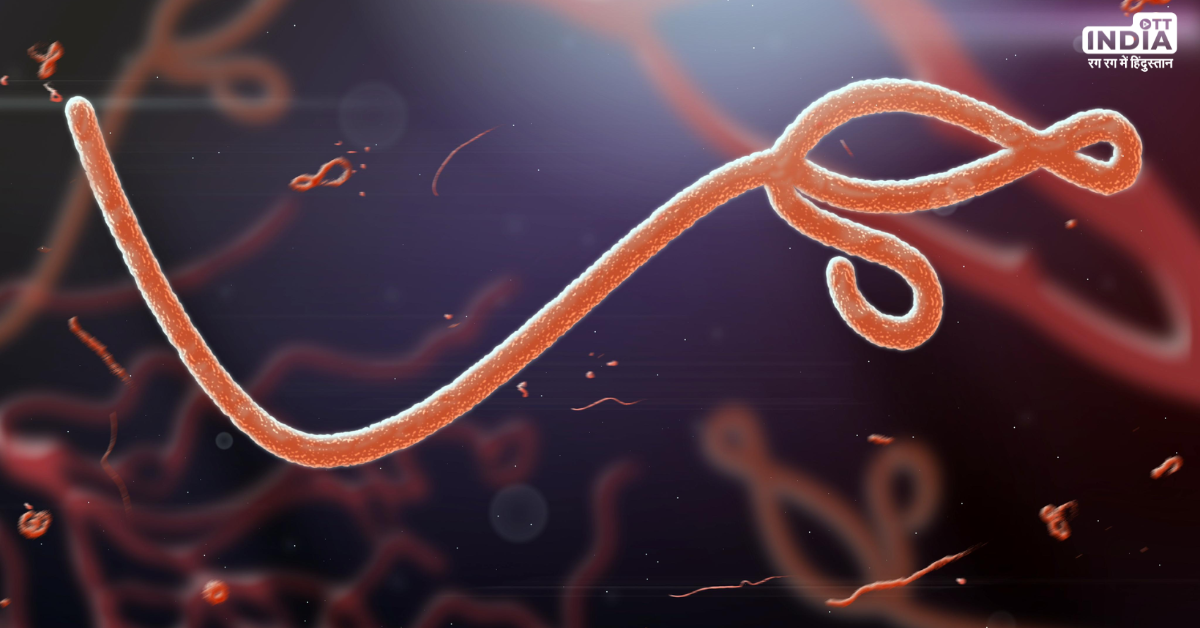
The Ebola Epidemics in West Africa:
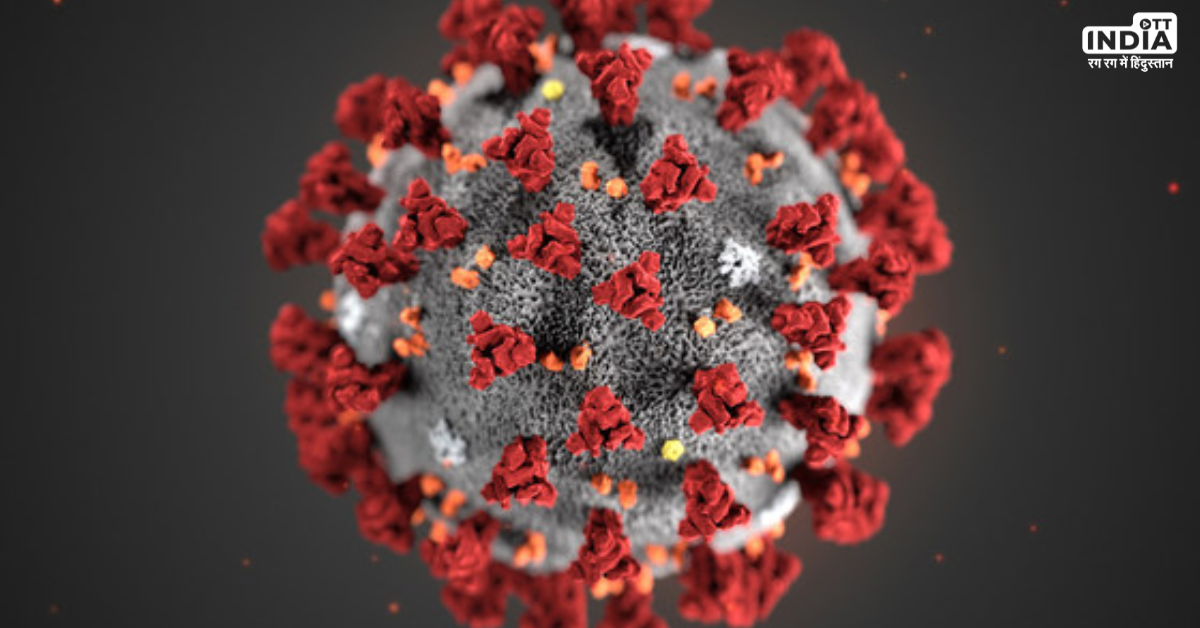
The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Wake-Up Call:
The Role of Preparedness and Surveillance:
To address the ongoing threat of emerging diseases, robust surveillance systems are crucial. Early detection, monitoring, and reporting of outbreaks enable swift responses to contain and mitigate the spread of diseases. Additionally, research into potential vaccines and treatments must continue, even in the absence of immediate threats.
Global Cooperation and Solidarity:
Emerging diseases do not respect borders, making global cooperation essential. International organizations, governments, healthcare workers, and researchers must collaborate to prevent, detect, and respond to outbreaks effectively. Sharing data, research, and resources across borders is key to managing emerging disease threats.
In conclusion, while we have made significant progress in understanding and combating emerging diseases, the battle is far from over. The world must remain vigilant, invest in healthcare infrastructure, and prioritize research to better prepare for future outbreaks. The COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated that, in the face of these threats, global solidarity and preparedness are our most potent weapons in safeguarding public health and preventing catastrophic outbreaks.
Also Read: Eating Your Way to Heart Health: Foods to Prevent Heart Diseases
OTT India updates you with the latest news, The Country’s no.1 digital news platform OTT India, Keeps you updated with national, and international news from all around the world. For more such updates, download the OTT India app on your Android and IOS device.
.





